Key Takeaways
- High home prices, interest rates, and inflation might make the market seem terrible, but much of that is hype.
- Interest rates are unlikely to decrease soon, with cuts not expected until the end of 2024.
- Current housing inventory is high, offering more choices for buyers and pressuring sellers to price realistically.
- Many listings are priced under $300,000, and reduced investor activity makes it a favorable time for first-time buyers.
- Buyers need to assess true market value amid price corrections and act proactively to find hidden opportunities.
In 2023, Austin experienced its first net population decline in a decade. This significant demographic shift has pushed Austin out of the top 10 largest U.S. cities. The population decline is largely attributed to high living costs and changing job market dynamics, which have made the city less attractive for both current residents and potential newcomers. As these factors continue to impact the city, Austin’s once booming growth is now facing a reversal, prompting concerns about its future sustainability and appeal. Here we will discuss why everyone is FLEEING Austin.
Major companies such as Oracle have moved their headquarters out of Austin, citing high operational costs and a lack of support for start-ups. Political and climate differences between California and Texas also played a role in these decisions. This corporate exodus has significantly impacted Austin’s real estate and job market. As these influential companies leave, the economic landscape of Austin is being reshaped, leading to further instability and uncertainty for residents and businesses.
Austin’s Rapid Growth Over the Past Decade
Austin’s transformation into a major tech hub brought with it an influx of new residents and businesses, leading to significant economic growth. The city became known for its innovative spirit and entrepreneurial culture, drawing talent and investment from across the country. This boom period saw Austin’s population swell, with new housing developments and business districts emerging to meet demand. Despite these positive developments, the rapid pace of growth also created pressures on housing and public services, leading to rising costs and congestion.
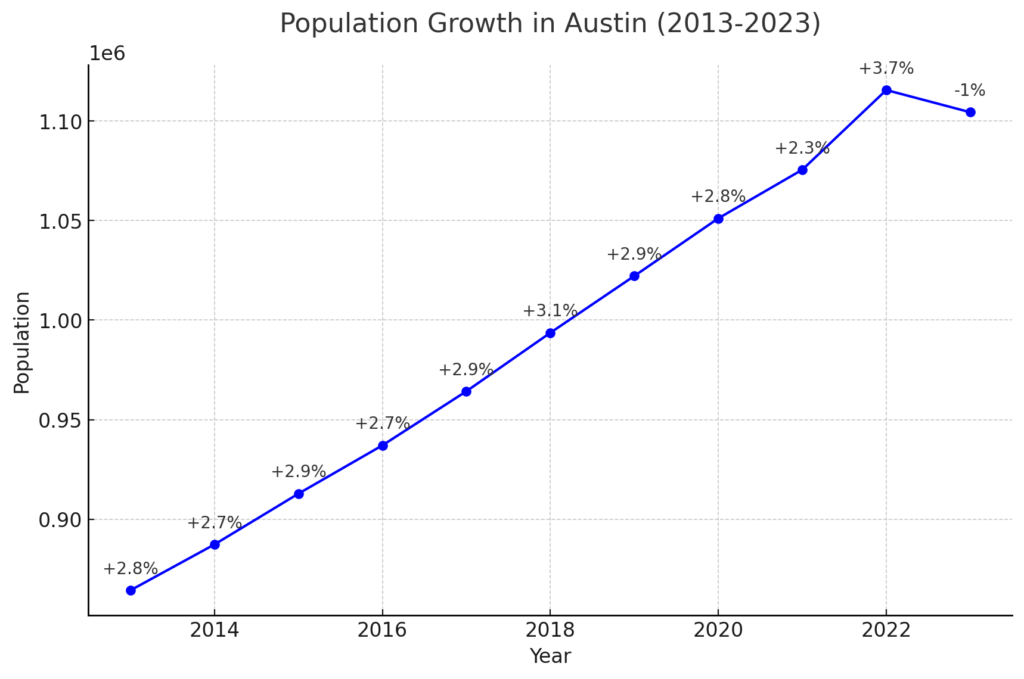
Booming Population Growth During the Pandemic
The pandemic spurred a population boom in Austin as remote work options expanded. High-income earners from states like California relocated to Austin, driving up housing demand and property prices. This rapid appreciation led to significant property tax increases and affordability issues for long-term residents. The market’s volatility raised concerns about long-term sustainability and potential corrections, making Austin less desirable for many who once saw it as an ideal place to live and work.
The influx of new residents during the pandemic also strained Austin’s infrastructure and resources. Schools, healthcare facilities, and transportation networks struggled to keep up with the rapid increase in population. This sudden growth highlighted the need for strategic urban planning and investment in public services to accommodate the expanding community. While the pandemic initially brought economic benefits, it also exposed vulnerabilities in Austin’s ability to manage rapid demographic changes effectively.
Skyrocketing Home Values
Austin’s home prices saw a dramatic increase during the pandemic, often doubling in a short period. This surge led to home values skyrocketing, causing financial strain for many residents. The rapid rise in prices has made it difficult for locals to afford housing, contributing to the population decline. As home values outpace incomes, the affordability crisis in Austin becomes more pronounced, driving residents to seek more affordable living options elsewhere.
The soaring home prices have also led to increased property taxes, further burdening homeowners. Many long-term residents, particularly those on fixed incomes, have found it challenging to keep up with the rising costs. This financial pressure has forced some to sell their homes and move to more affordable areas. The housing market’s volatility has created uncertainty, with potential buyers and investors wary of potential corrections that could impact property values in the future.
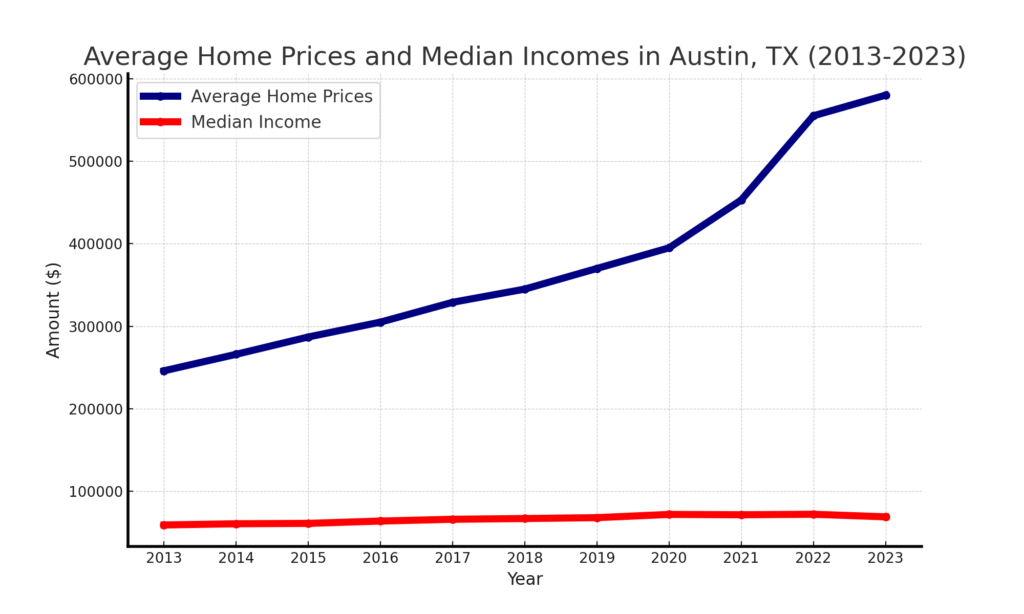
High Home Values Outpacing Median Incomes
Home values in Austin have increased significantly faster than median incomes, creating a disparity that makes the city less affordable. This growing gap has prompted some residents to leave in search of more affordable housing. The high cost of living in Austin now exceeds the financial reach of many middle-class families, leading to a population decline as people move to areas with a more balanced cost of living.
The affordability crisis has hit renters particularly hard, with rent prices rising alongside property values. Many residents are spending a larger portion of their income on housing, leaving less for other necessities. This financial strain has contributed to a decrease in the quality of life for many Austinites. As the cost of living continues to rise, more families are considering relocating to more affordable regions, exacerbating the population decline.
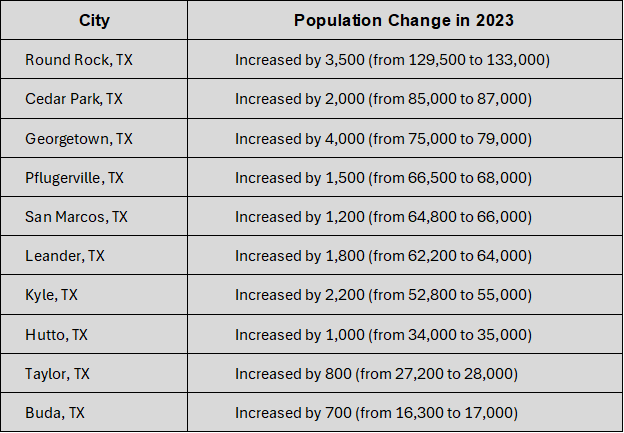
Continued Growth in Surrounding Counties (Williamson, Hays)
Williamson and Hays counties are experiencing a population boom as people move away from Austin in search of more affordable housing. These areas offer new construction and promotional interest rates, attracting new residents. Suburban growth provides an alternative for those priced out of Austin’s housing market. As Austin’s affordability declines, surrounding counties benefit from the influx of residents seeking better living conditions and lower costs.
Lost Creek Neighborhood De-Annexation
Residents of Lost Creek are considering de-annexation due to rising property crime and dissatisfaction with the Austin Police Department’s response. To address their concerns, they have hired private security, highlighting a significant trust gap with local law enforcement. De-annexation efforts underscore broader concerns about safety and governance in Austin. The push for de-annexation reflects a growing sentiment among residents that the city’s services are failing to meet their needs.
The de-annexation movement in Lost Creek is part of a larger trend of communities seeking greater control over their governance and resources. Residents argue that local authorities have not adequately addressed their concerns about crime and safety. By de-annexing, they hope to implement more effective security measures and improve community oversight. This move highlights the challenges cities face in balancing growth with the provision of essential services and maintaining public trust.
Political Ideologies Influencing Tech Firms’ Decisions to Leave
Political factors, including conservative policies, are influencing tech firms’ decisions to leave Austin. Differences in state policies, such as those on abortion and climate regulations, create a challenging environment for some companies. The political environment in Texas contrasts sharply with the progressive values of many tech workers, prompting companies to seek locations with policies that better align with their corporate cultures and employee preferences.
The departure of tech firms from Austin reflects broader tensions between business interests and political climates. Companies that prioritize diversity and progressive policies may find it challenging to operate in states with conservative legislative agendas. As firms evaluate their locations based on employee preferences and corporate values, states with policies that support inclusivity and sustainability may become more attractive. This shift has significant implications for the economic landscape of cities like Austin, which have relied on the tech industry for growth.
Economic, Cultural, and Political Factors for Tech Companies in Austin, TX
- Political Climate Impact discusses how the conservative political climate in Texas, including strict laws on healthcare and abortion, affects tech workers’ and companies’ decisions to remain in or leave the state.
- Cultural Clash highlights the cultural and ideological clash between the progressive values held by many in the tech industry and the conservative policies prevalent in Texas.
- Personal Impact emphasizes personal anecdotes and opinions from tech workers who feel alienated by the state’s political environment, influencing their decision to relocate.
- Rising Costs outlines the increasing cost of living and operating expenses in Austin, which are driving tech companies to consider moving to more affordable locations.
- Economic Factors examines how economic factors such as access to capital, housing prices, and operational costs influence tech firms’ decisions to leave Austin.
- Business Climate discusses the broader business climate in Austin, including the challenges and opportunities that come with the rapid growth of the tech sector in the city.
- Brand-Consumer Relationships reviews how political ideologies impact relationships between consumers and brands, highlighting the importance of political neutrality to avoid alienating moderate consumers.
- Corporate Activism discusses the role of corporate activism and how companies’ political affiliations can influence their brand perception and consumer loyalty.
- Strategic Implications provides insights into the strategic implications for businesses, suggesting that firms need to carefully navigate political ideologies.
Stabilization of the Housing Market Post-Pandemic Boom
The housing market in Austin is stabilizing after the pandemic boom, with buyers becoming more cautious. This shift is leading to longer times on the market and fewer bidding wars. The market correction offers opportunities for strategic buyers and investors. Despite the cooling market, understanding true property values can help buyers make informed decisions and capitalize on potential negotiation opportunities in Austin’s evolving real estate landscape.
As the market stabilizes, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable development and affordable housing solutions. Policymakers and developers are working together to create housing options that meet the needs of a diverse population. This includes initiatives to increase the availability of affordable rental units and support for first-time homebuyers. By addressing the underlying issues that contributed to the housing boom and bust, Austin can build a more resilient and inclusive housing market for the future.
Final Thoughts
Despite the perceived downturn, there are still market opportunities for savvy buyers and investors in Austin. Homeowners tend to overvalue their properties, creating potential negotiation opportunities for buyers. Understanding true market values can help buyers make informed decisions in a cooling market. For those willing to navigate the current landscape, Austin still presents investment opportunities amid the shifting economic and demographic trends.
History of Tech in Austin
- 1960s: University of Texas establishes computer research center.
- 1980s: The Rise of Silicon Hills
- MCC–Microelectronics and Computer Consortium– established in 1982 as the first, and at that time, largest, industry-led research consortium for microelectronics and computer technology.
- Major companies: IBM, Texas Instruments, and AMD establishing operations
- 1990s: The Dot-Com Boom
- Key players: Dell, Tivoli Systems, and Vignette Corporation
- 2000s: Diversification and Growth
- Post-dot-com diversification: the rise of gaming and creative technology industries
- Prominent companies: Blizzard Entertainment, BioWare, and Apple
- 2010s: The Startup Boom
- Surge in tech startups and entrepreneurial activity
- Role of incubators and accelerators: Capital Factory, Techstars
- Tech Giants and Corporate Relocations
- Major relocations: Google, Facebook, Tesla, and Oracle establishing significant operations
- The Role of Events and Conferences
- South by Southwest (SXSW) and its impact on tech innovation
- Austin Startup Week and other local events fostering tech community
Tech Companies in Austin with over 5,000 Employees
- Dell Technologies – 165,000 employees
- IBM – 345,000 employees
- Apple – 154,000 employees
- Google – 190,000 employees
- Oracle – 132,000 employees
- Tesla – 127,000 employees
- Facebook (Meta) – 86,482 employees
- Amazon – 5,000 employees

